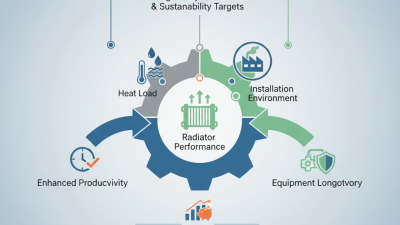
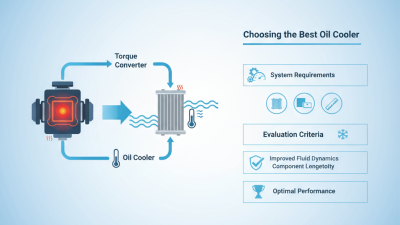
As industries continue to evolve, the significance of effective thermal management becomes increasingly critical to optimizing performance and efficiency. In this context, Industrial Radiators emerge as essential components designed to enhance heat dissipation, contributing to the overall operational efficiency of various systems. With advancements in technology and design, industrial radiators not only allow for better thermal regulation but also enable industries to comply with stricter environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
The insights gathered for 2025 highlight the innovative trends and key factors influencing the performance of Industrial Radiators. These insights encompass everything from materials and design configurations to cutting-edge techniques aimed at maximizing heat transfer efficiency. As industries seek to improve their processes and reduce energy consumption, understanding the dynamics of Industrial Radiators becomes imperative for engineers and decision-makers alike.
The upcoming sections will delve into the latest developments, best practices, and critical considerations manufacturers and users must address in order to select and implement the most efficient Industrial Radiators tailored to their specific needs. By leveraging these insights, stakeholders can pave the way for enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs in their respective sectors.
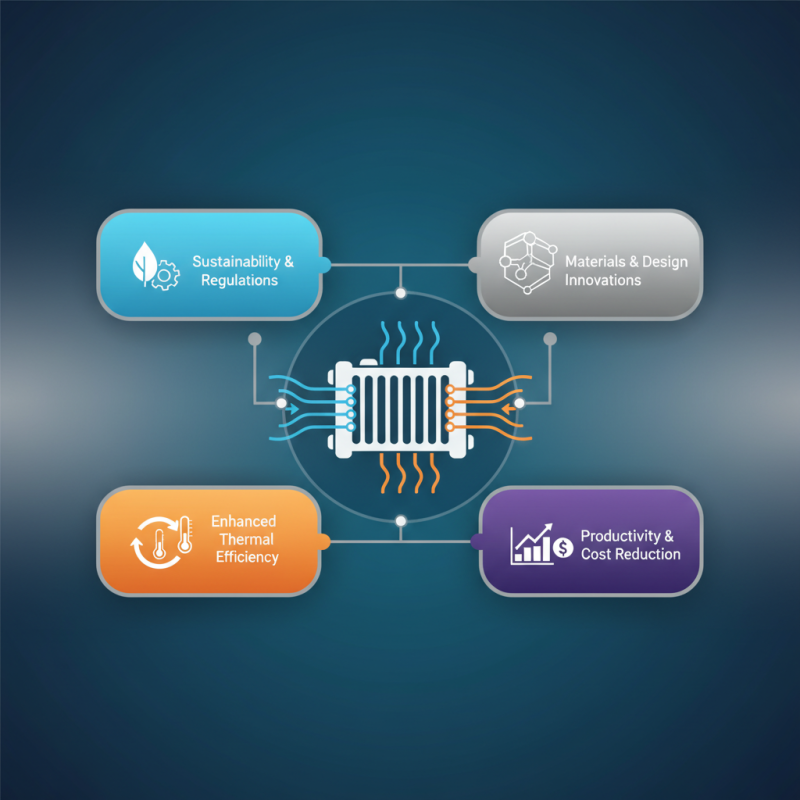
Industrial radiators are critical components that play a pivotal role in enhancing performance and ensuring optimal efficiency in various industrial applications. The essential components of these radiators include the core structure, fins, and tubing systems. The core structure serves as the main heat exchanger, where heat is absorbed from the fluid that needs to be cooled or heated. This component’s design is crucial as it dictates the thermal efficiency of the radiator. A well-constructed core can maximize the surface area available for heat transfer, allowing for improved performance.
Fins attached to the core structure are equally important as they enhance the heat dissipation capabilities of the radiator. These fins increase the surface area exposed to air or coolant, facilitating more efficient heat exchange. The material and design of the fins—whether they are flat, corrugated, or louvered—impact the airflow and ultimately affect the cooling performance. Additionally, the tubing systems that circulate the fluid through the radiator are critical for maintaining a consistent temperature and ensuring optimal flow rates. The choice of materials and the diameter of the tubes can significantly influence the efficiency of heat transfer and the overall longevity of the radiator.
By carefully considering these essential components and their interrelationships, industrial facilities can optimize their operations and improve energy efficiency. A well-designed radiator not only enhances performance but also contributes to the reliability and durability of the entire system, making it a vital investment for any industrial process.
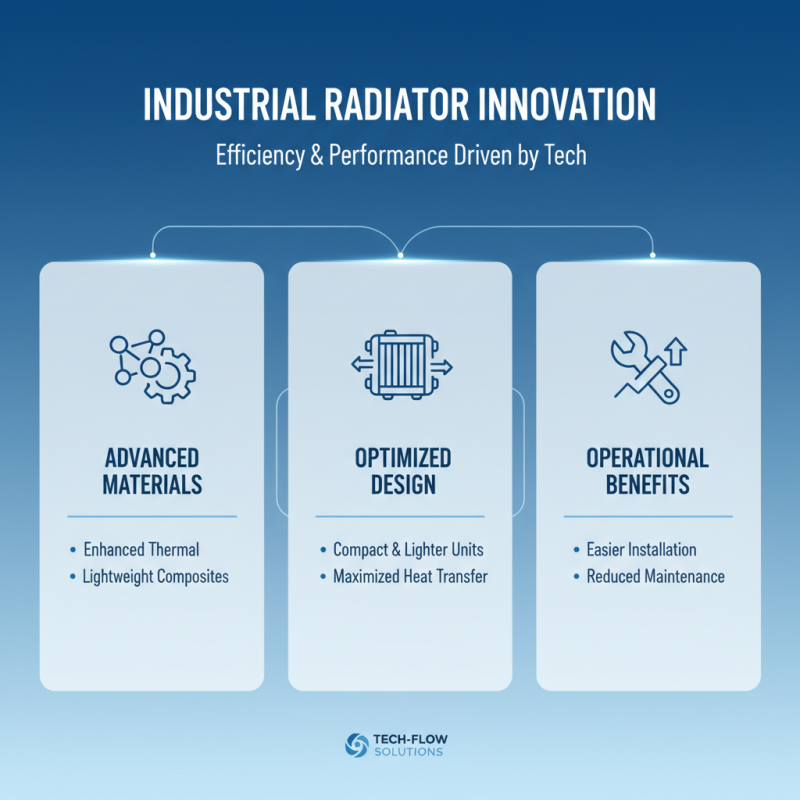
The design of industrial radiators is undergoing significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology aimed at enhancing efficiency and performance. One of the key technologies is the implementation of improved heat exchange materials that maximize thermal conductivity while minimizing weight. This not only optimizes the heat transfer process but also allows for designs that are more compact and lightweight, which can lead to easier installation and maintenance in various industrial settings.
Another important aspect influencing the efficiency of industrial radiators is the integration of smart sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities. By leveraging real-time data, these systems can monitor temperature, pressure, and flow rates, allowing for precise adjustments to maintain optimal operating conditions. This responsiveness contributes to reduced energy consumption and prolonged equipment lifespan. Furthermore, advancements in simulation software have enabled engineers to model and test radiator designs more effectively, ensuring that the final products deliver maximum performance and efficiency throughout their operational life. These technological innovations are setting new benchmarks for industrial radiator performance, providing industries with effective solutions for their heating and cooling needs.
Maintaining and optimizing industrial radiators is crucial for ensuring their efficiency and longevity. Regular inspections are essential to identify any signs of corrosion, leaks, or blockages that may hinder performance. Operators should establish a routine maintenance schedule that includes cleaning the radiator fins, checking the coolant levels, and ensuring that the fan and motor are functioning correctly. This proactive approach can help prevent issues from escalating, which can lead to costly downtime and repairs.
In addition to regular inspections, implementing best practices for operation can significantly enhance radiator performance. This includes monitoring the operating temperature closely and adjusting the system as required to prevent overheating. Ensuring that the surrounding environment is free from dust and debris can also improve airflow, allowing the radiator to operate more efficiently. Furthermore, employing advanced monitoring systems can provide real-time data on radiator performance, enabling prompt responses to any anomalies. By prioritizing these maintenance and optimization strategies, industrial facilities can achieve optimal efficiency and prolong the lifespan of their radiators.

As we look forward to 2025, the landscape of industrial radiator technology is undergoing significant transformation driven by innovation and sustainability. One notable trend is the integration of advanced materials that enhance thermal efficiency and reduce weight. For example, the use of composites and high-performance alloys not only improves heat transfer but also extends the lifespan of radiators, ultimately leading to lower operational costs. These innovations are critical for industries aiming to boost energy efficiency while minimizing their environmental footprint.
Moreover, the advent of smart radiator systems is set to revolutionize the market. By incorporating IoT technology, these systems enable real-time monitoring and automated adjustments based on individual operational needs. This level of adaptability enhances performance, as environments can change rapidly and demand immediate responses to maintain optimal thermal management. Predictive maintenance features will also play a crucial role, helping facilities avoid unexpected downtimes and costly repairs while ensuring that their equipment runs at peak efficiency. As these trends continue to evolve, they underscore the importance of adaptability and foresight in industrial infrastructure planning for the coming years.
In recent years, the adoption of efficient radiator systems has yielded significant improvements in various industrial applications. A notable case study involved a chemical manufacturing plant, which implemented a state-of-the-art radiator system designed to enhance heat transfer performance while minimizing energy consumption. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), industries could reduce energy use by up to 30% with the adoption of optimized heat exchange systems, showcasing the potential for both cost savings and environmental benefits. The plant reported a 25% decrease in operational costs and a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, validating the efficacy of these upgraded systems.
Another compelling example comes from a food processing facility that faced challenges with temperature management and product quality control. After transitioning to a high-efficiency radiator system, the facility achieved a temperature regulation improvement of nearly 15%. This transformation resulted in a significant increase in product yield and consistency. The U.S. Department of Energy highlighted similar findings in their recent publication, noting that improved radiator systems can boost industrial process efficiency by up to 40%, leading businesses to not only enhance performance but also position themselves as leaders in sustainable practices. Implementing these advanced technologies is becoming increasingly vital for industries aiming to meet both operational and regulatory standards.