The evolving landscape of thermal management technologies is marked by the rise of the Microchannel Heat Exchanger. These devices are crucial for enhancing energy efficiency across various sectors. Their compact design offers significant advantages in heat transfer performance. A key benefit is the reduction in refrigeration load, leading to lower energy consumption. This is vital in industries like HVAC and automotive.
Innovations in 2026 showcase remarkable advancements. Manufacturers are developing more effective materials and designs. Enhanced fabrication techniques allow for better fluid distribution and heat transfer. These innovations pave the way for applications in electric vehicles and more efficient cooling systems. However, challenges remain in scalability and cost-effectiveness.
The potential of Microchannel Heat Exchanger technology is vast. Yet, it requires ongoing research and collaboration to overcome existing limitations. Markets demand affordable, high-performance thermal solutions. Balancing innovation with practical application will be necessary for the future. Establishing industry standards will also help guide development and ensure consistency.

The advancements in microchannel heat exchanger technology for 2026 are remarkable. New designs are pushing boundaries. These innovations aim to address efficiency issues. Reports suggest a potential 30% increase in thermal performance. This is crucial for industries relying on effective heat management.
Enhanced manufacturing techniques are reshaping the landscape. Precision engineering reduces waste and increases reliability. Research highlights that microchannel systems can operate at higher pressures without failure. However, achieving such durability remains a challenge. Some prototypes have not yet reached expected life spans in rigorous environments.
Real-world applications are expanding, particularly in HVAC and automotive sectors. Estimated energy savings could reach 15% when integrated correctly. Still, more work is needed to optimize these systems for various applications. The potential is vast, but the industry faces hurdles in scaling these innovations efficiently. Each advancement presents lessons to reconsider.
Microchannel heat exchangers (MCHEs) are gaining traction in various industries. These devices offer efficient heat transfer, compact design, and lower refrigerant charges. Emerging applications are transforming traditional processes, particularly in HVAC and automotive sectors.
In the automotive industry, MCHEs are improving thermal management systems. Their small size allows for lighter vehicle designs. This translates to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. However, challenges remain, such as the need for robust materials that can withstand harsh environments. There is still room for improvement in heat exchanger durability.
Another intriguing application is in renewable energy. MCHEs can enhance the efficiency of solar thermal systems. Their compact nature allows for integration into small spaces. However, the technology must overcome cost barriers and scaling issues. It’s essential to research long-term performance and potential ~maintenance pitfalls. The industry must remain flexible, embracing innovations while addressing these critical challenges.
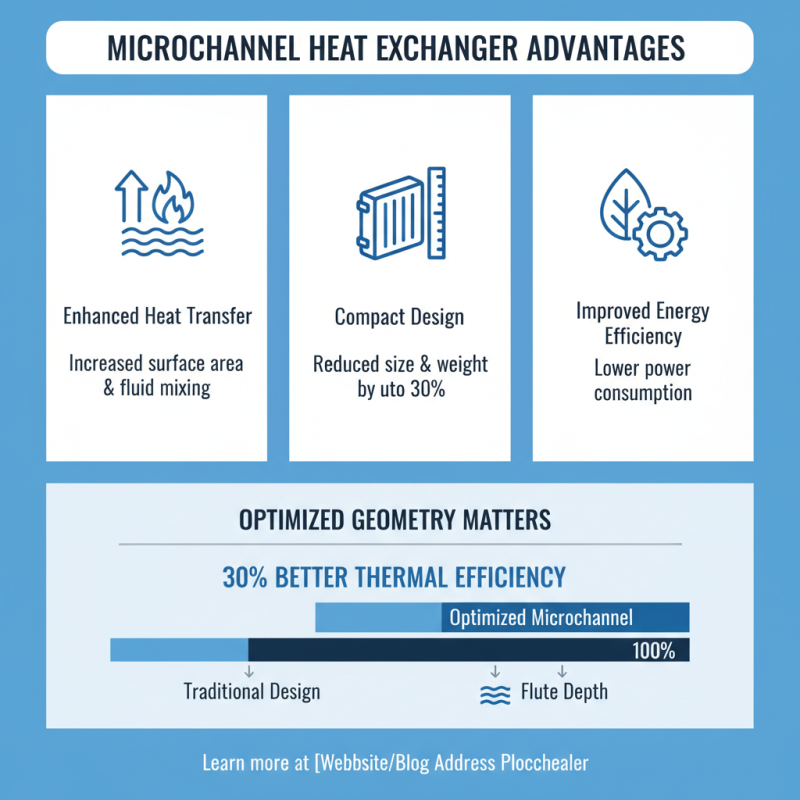
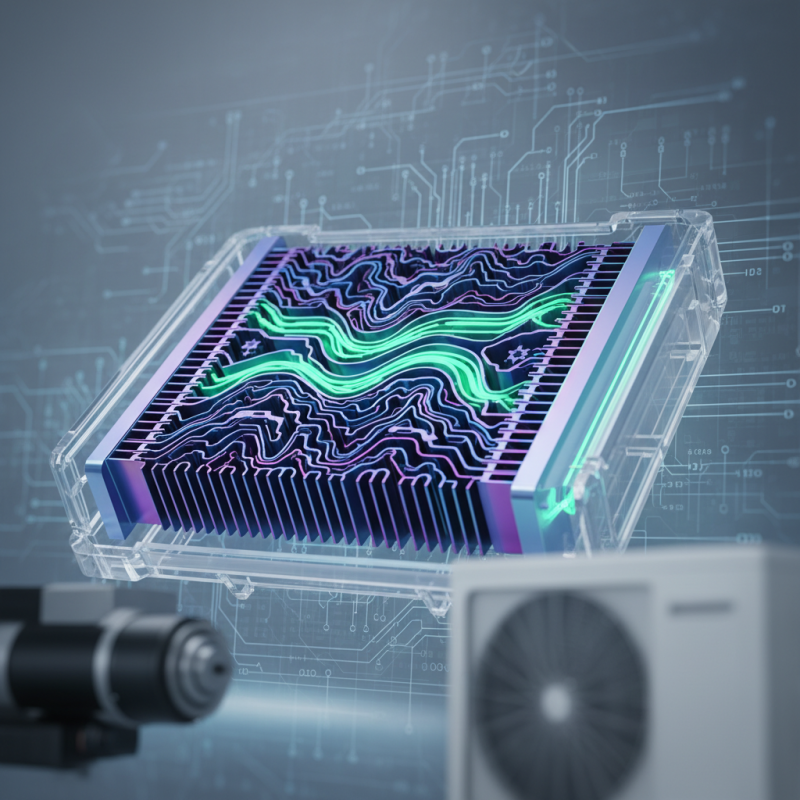
Microchannel heat exchangers (MCHEs) have gained significant traction in recent years. They offer enhanced heat transfer capabilities, compact designs, and improved energy efficiency. A comparative analysis of various microchannel designs reveals that flute width and depth play a critical role in performance. Reports indicate that optimized microchannel geometries can improve thermal efficiency by nearly 30% compared to traditional designs.
Furthermore, pressure drop is another crucial metric. Some designs, while efficient, may incur higher pressure losses. Such trade-offs need careful consideration. For instance, a study found that the optimal balance between heat transfer and pressure drop can lead to an efficiency gain of up to 25%. This demonstrates a vital area for improvement and reflection in microchannel design strategies.
Tip: Regularly evaluate heat exchanger performance metrics. Adjusting flow rates and temperatures can yield surprising efficiency gains.
Continual development in microchannel designs is essential. Innovations like additive manufacturing are pushing boundaries. Yet, not all advancements yield immediate improvements in efficiency. Some may require extensive testing and validation. Therefore, manufacturers should approach new designs with a critical eye, weighing both benefits and potential drawbacks.
The integration of smart technologies into microchannel heat exchangers is transforming cooling and heating systems. These innovations enhance efficiency and optimize performance. For instance, sensors can monitor temperature and flow rates in real-time. This data allows for precise adjustments, improving energy use and performance.
However, challenges remain. Not every installation can support these smart devices. Some existing systems may lack the necessary infrastructure. This can hinder the full realization of smart technology benefits. Moreover, data security is a concern. Ensuring safe communication between devices is critical.
Despite these challenges, the potential is immense. Predictive maintenance can extend the life of heat exchangers. Smart algorithms can identify issues before they escalate. This shift towards smarter management of thermal systems is underway, yet it requires careful consideration of integration methods. Balancing innovation with practicality is key for successful implementation.
| Innovation | Description | Application Area | Smart Technology Integration | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Heat Transfer Fluids | Utilization of new fluids for improved thermal conductivity. | HVAC Systems | Real-time monitoring sensors | Increased efficiency and reduced operational costs |
| 3D Printed Microchannels | Manufacturing of complex geometries for enhanced heat transfer. | Automotive Cooling Systems | AI-based design optimization | Reduced weight and improved performance |
| Modular Microchannel Units | Flexible design allowing for easy modification and maintenance. | Data Centers | IoT connectivity and analytics | Enhanced scalability and reduced downtime |
| Nanotechnology Coatings | Improved surface properties for better heat exchange. | Industrial Refrigeration | Smart analytics for predictive maintenance | Longer equipment life and energy savings |
| Integrated Control Systems | Seamlessly managing heat exchange processes with minimal human intervention. | Renewable Energy Applications | Autonomous control technology | Improved energy efficiency and productivity |
Microchannel heat exchangers are making waves in sustainability efforts. Their compact design enhances efficiency, reducing energy consumption. According to recent reports, they can achieve up to 40% higher heat transfer rates compared to traditional designs. As industries face increasing pressure to minimize carbon footprints, these innovations present viable solutions.
The manufacturing process for microchannel exchangers is not without challenges. While they save energy, their production can generate waste. It's crucial to adopt practices that mitigate environmental impact. For example, using recyclable materials can help balance the equation. Additionally, companies should invest in cleaner technologies to produce these components.
Tip: Consider local materials for manufacturing to reduce transportation emissions. The environmental benefits are significant, but sustainability must be woven into every step of production.
While microchannel designs hold promise, they require careful evaluation. New technologies may introduce unforeseen issues, such as maintenance difficulties. Implementing regular review processes can ensure long-term viability and customer satisfaction. This diligence will help the industry evolve responsibly.