In recent years, the demand for efficient cooling solutions has surged across various industries. Microchannel Heat Exchangers (MCHXs) have emerged as an innovative technology to address this need. According to a 2022 market report by Frost & Sullivan, the MCHX market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.5% through 2027. These compact heat exchangers offer superior thermal performance with a smaller footprint, making them ideal for applications in automotive, HVAC, and electronics cooling.
Dr. Emily Carter, an expert in thermal systems, emphasizes the significance of MCHXs in modern cooling technologies: “Microchannel designs are revolutionizing how we think about efficiency.” This statement highlights the paradigm shift occurring in cooling solutions. Companies are increasingly recognizing the advantages of reducing energy consumption while maximizing cooling efficiency.
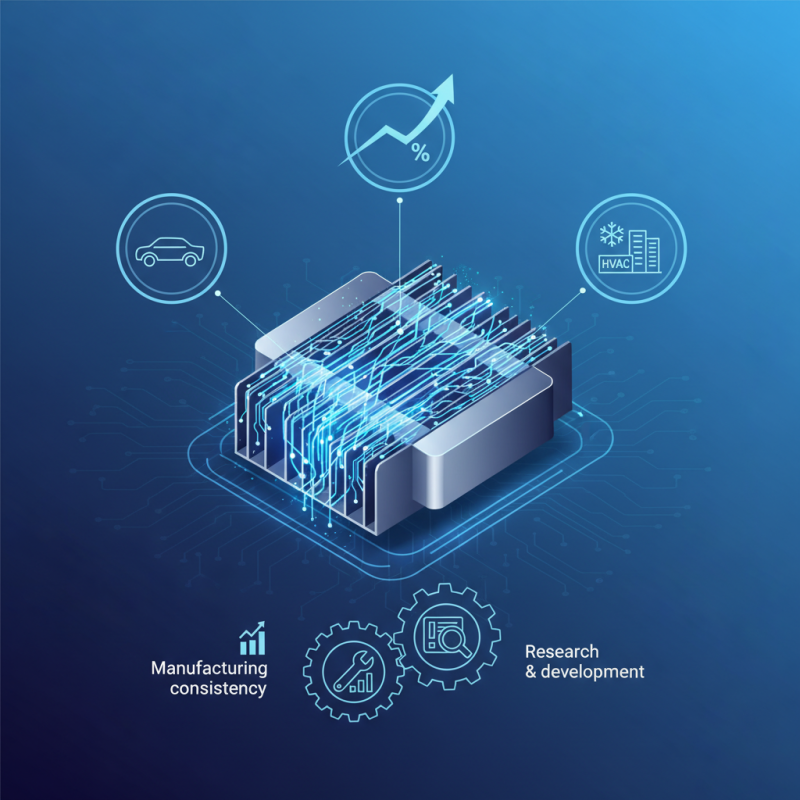
However, there are challenges. Issues such as manufacturing consistency and material reliability are areas needing improvement. Engineers must carefully design and test MCHXs to ensure optimal performance. As the industry evolves, continuous research and development are vital for overcoming these hurdles. The progress in MCHXs illustrates both the potential and the complexities inherent in adopting new technologies.

Microchannel heat exchangers are essential for efficient cooling in various applications. These compact devices utilize a network of small channels to enhance heat transfer. This design allows for a larger surface area, resulting in improved thermal performance. They are widely used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and automotive industries.
The applications of microchannel heat exchangers are diverse. In automotive cooling systems, they contribute to engine efficiency and reduced emissions. In industrial settings, they are used for cooling machinery and process temperatures. However, there are challenges. Maintenance can be complex due to the intricate design. Over time, these systems may suffer from fouling and corrosion.
Integrating microchannel technology requires careful consideration. Not every system may benefit from their compact design. Their initial cost can be higher, potentially offsetting savings on energy efficiency. Understanding the balance between performance and investment is crucial for optimal outcomes.
Microchannel heat exchangers have gained attention for their efficiency in cooling solutions. These advanced exchangers utilize multiple small channels instead of traditional designs. This structure allows for a larger surface area, improving heat transfer and reducing the size of the unit. Reports indicate that these systems can be up to 30% more efficient than conventional options.
Key features of microchannel heat exchangers include their lightweight design. This can significantly reduce the overall weight of cooling systems. They also support reduced refrigerant charge requirements, promoting sustainability. However, it's important to note that these units can be more sensitive to fouling and corrosion. Regular maintenance checks are crucial to ensure longevity.
Tip: Consider integrating corrosion-resistant materials for better durability. Regular inspections can help identify potential fouling. Another point for reflection is that while their initial cost might be higher, the long-term savings in energy efficiency can justify the investment. Understanding these dynamics can lead to better decision-making in cooling solutions.
| Model | Cooling Capacity (kW) | Material | Efficiency (%) | Application | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 35 | Aluminum | 90 | HVAC | 15 |
| Model B | 40 | Copper | 92 | Industrial | 18 |
| Model C | 30 | Stainless Steel | 87 | Automotive | 20 |
| Model D | 25 | Titanium | 95 | Marine | 22 |
| Model E | 45 | Aluminum | 88 | Telecom | 19 |
In 2026, microchannel heat exchangers stand out for efficient cooling. These systems enhance heat transfer, making them popular in HVAC and automotive applications. Their compact size and lightweight design allow for better integration into various setups, saving space without sacrificing performance.
When selecting a microchannel heat exchanger, consider the material used. Aluminum is common, offering good thermal conductivity. However, some users might overlook corrosion resistance. This can lead to failures over time. Look for products with protective coatings to prevent this issue.
Also, pay attention to the flow arrangement. Parallel flow configurations may improve heat transfer efficiency. But they might not always be the best choice for every application. Explore different options to find what works best for your needs.
Tips: Regular maintenance can prolong the life of your heat exchanger. Keep an eye on any signs of wear or leakage. Efficient cooling is invaluable, but ensuring longevity is equally important.
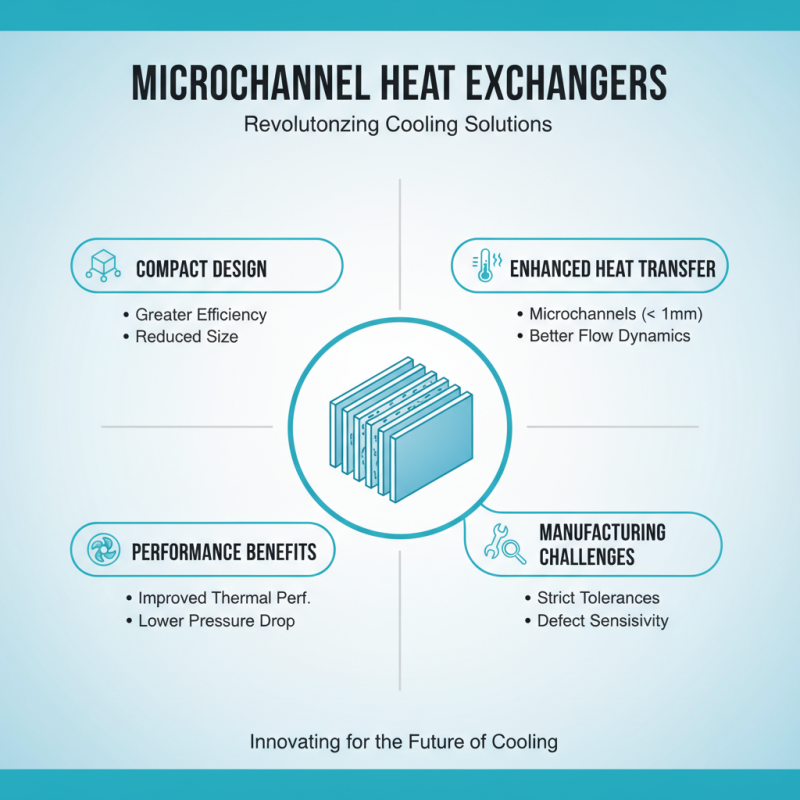
Microchannel heat exchangers are revolutionizing cooling solutions. Their compact design allows for greater efficiency in heat transfer. The microchannels, typically measuring less than 1 mm in diameter, enable better flow dynamics. This results in reduced pressure drops and improved thermal performance. However, the design intricacies also raise challenges. Manufacturing tolerances must be strict to ensure optimal functionality. Small defects can significantly impact efficiency.
Researchers have compared various microchannel designs. Some layouts enhance surface area while maintaining a minimal footprint. Others focus on fluid distribution, which influences heat transfer rates. Certain configurations do not perform as expected, revealing areas for improvement. The effectiveness of these designs often depends on the specific application. This can lead to discrepancies in performance that require careful assessment.
Material selection plays a crucial role in efficiency. Some materials demonstrate excellent thermal conductivity but are prone to corrosion. Others may be durable yet less efficient in heat exchange. These factors complicate the decision-making process. Engineers must balance cost, durability, and performance. Ultimately, the quest for the best microchannel heat exchanger design continues, as innovations persist.
The future of microchannel heat exchanger technology is bright, yet it faces several challenges. Innovations are emerging, focusing on enhanced efficiency and compact designs. Microchannels offer reduced cooling medium volumes, but can they handle high flow rates effectively? Engineers are experimenting with designs for better flow distribution.
The integration of advanced materials is another trend. Researchers explore lighter and more conductive materials to reduce weight. This could lead to improved thermal performance. However, the durability of these new materials needs scrutiny. Testing under real-world conditions often reveals unforeseen issues.
Another exciting development is the use of additive manufacturing. This technology allows for complex geometries impossible with traditional methods. Customization may meet specific cooling requirements more effectively. Yet, the long-term reliability of additively manufactured components is still under evaluation. Each innovation brings hope, but also demands careful assessment and refinement.