In the quest for enhanced energy efficiency and superior thermal performance, Microchannel Heat Exchangers have emerged as a pivotal innovation in the cooling solutions market. According to a report by Global Market Insights, the microchannel heat exchanger market is poised for significant growth, projected to reach a valuation of over $1 billion by 2026, as industries increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability. The compact design of microchannel heat exchangers allows for a higher surface area-to-volume ratio, which translates into improved heat transfer efficiency compared to traditional heat exchanger designs.
Moreover, the adoption of Microchannel Heat Exchangers is spurred by the growing demand for lightweight and efficient cooling solutions in various applications, including HVAC systems, automotive air conditioning, and industrial cooling processes. Research conducted by the U.S. Department of Energy indicates that microchannel technology can reduce refrigerant charges by up to 50%, leading to lower operational costs and a reduced environmental footprint. As the industry shifts towards embracing innovative solutions, Microchannel Heat Exchangers stand out as a reliable choice for achieving energy optimization and meeting the increasing regulations on energy consumption and emissions.
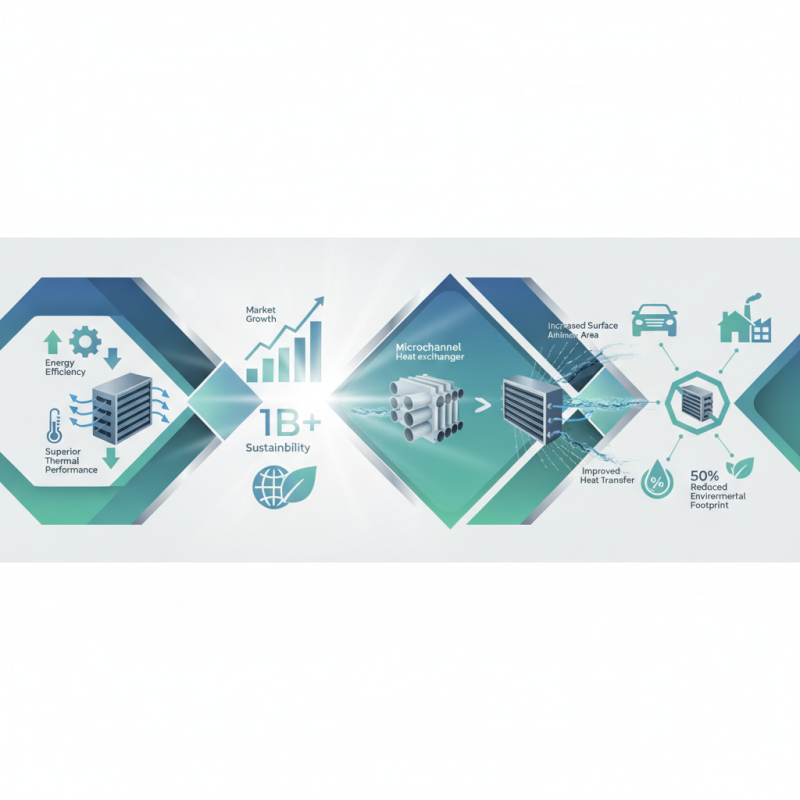
Microchannel heat exchangers are becoming increasingly popular in cooling applications due to their enhanced efficiency and compact design. These heat exchangers feature a series of small, parallel channels that significantly increase the surface area for heat transfer. Their design principles revolve around optimizing fluid flow to improve thermal performance. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, microchannel systems can achieve energy savings of up to 30% compared to traditional heat exchangers, particularly in HVAC and refrigeration applications. This efficiency is largely attributed to their ability to minimize refrigerant charge and reduce pressure drops.
One of the key design principles of microchannel heat exchangers is the use of thin-walled tubes, which allow for a greater heat transfer coefficient. This design not only enhances the overall efficiency but also contributes to a reduction in the size and weight of the unit. Research shows that microchannel heat exchangers can deliver thermal efficiency improvements of around 20% to 50% over conventional models, depending on the application and operating conditions. The compact footprint also makes them ideal for space-constrained environments, making them a preferred choice for modern cooling systems where efficiency and size are paramount considerations. As industries increasingly seek sustainable and energy-saving solutions, microchannel heat exchangers are positioned to play a critical role in achieving these goals.
Microchannel heat exchangers have gained popularity in cooling applications due to their compact and efficient design. One of the primary benefits is their enhanced heat transfer performance. The microchannel structure, characterized by numerous small channels, increases the surface area for heat exchange, allowing for more efficient thermal management. This is particularly advantageous in scenarios where space is limited, as these heat exchangers can deliver effective cooling without requiring large volumes of cooling fluids.
Another significant advantage of microchannel heat exchangers is their reduced weight and footprint compared to traditional heat exchanger designs. This lightweight construction not only simplifies installation but also facilitates integration into various systems, including HVAC and industrial equipment. Additionally, the smaller volume of refrigerant needed helps minimize environmental impact, making microchannel heat exchangers a more sustainable option. The combination of high efficiency, reduced environmental footprint, and versatility makes them an ideal choice for modern cooling solutions across diverse applications.
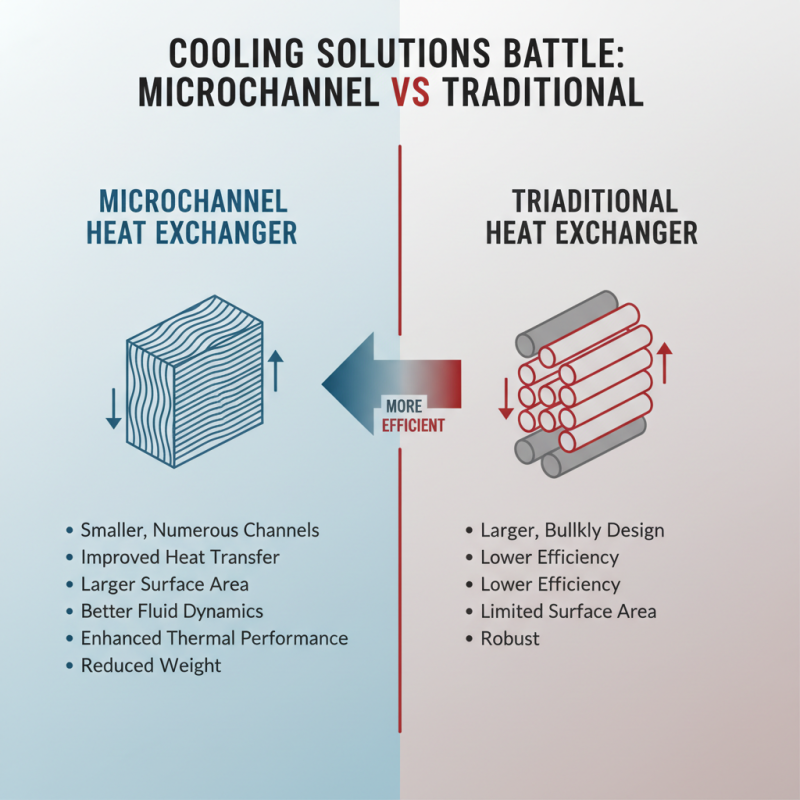
When it comes to cooling solutions, the battle between microchannel and traditional heat exchangers is ongoing. Microchannel heat exchangers utilize smaller and more numerous channels, significantly improving the heat transfer efficiency compared to their traditional counterparts. This design allows for a larger surface area and better fluid dynamics, resulting in enhanced thermal performance and reduced weight. Traditional heat exchangers, while robust, often suffer from lower efficiency due to their larger, bulkier designs and limited surface area.
Tips: When evaluating cooling solutions, consider the application’s specific needs. Microchannel heat exchangers are ideal for environments where space is a constraint, offering compact solutions without sacrificing performance. Furthermore, their ability to operate effectively at lower fluid levels can reduce operating costs, an advantage not always found with traditional systems.
On the other hand, traditional heat exchangers may still have their place in applications where durability and simplicity are paramount. They can easily handle high fluid flow rates and are proven designs, making them suitable for certain industrial applications. However, as efficiency standards rise, more industries are leaning towards the advanced benefits of microchannel technology. When assessing these two types, understanding the unique demands of your application can lead to more informed decisions on the best cooling solutions available.
Microchannel heat exchangers are making significant strides across various industries, primarily due to their compact design and higher efficiency. In the HVAC sector, these heat exchangers have been adopted to enhance cooling performance in both residential and commercial applications. With the ability to operate effectively in tighter spaces, microchannel technology allows for a reduction in material use while maintaining optimal thermal control. This advancement not only results in lower energy consumption but also contributes to more sustainable building practices.
The automotive industry is also seeing increased implementation of microchannel systems, particularly in vehicle air conditioning and engine cooling applications. These heat exchangers facilitate faster heat transfer, which is crucial for managing the rising temperatures associated with modern engines. As vehicles become more fuel-efficient, the need for effective cooling solutions becomes even more critical, positioning microchannel technology as a key player in enhancing vehicle performance. Furthermore, the electronics sector leverages microchannel heat exchangers for thermal management of high-performance computing systems, where efficient cooling is essential to ensure reliable operation and longevity of components.
The landscape of microchannel heat exchangers is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing demands for energy efficiency and compact designs in various industries. As technology progresses, new materials and manufacturing techniques are enabling the development of microchannel systems that offer superior thermal performance while minimizing weight and volume. These innovations are crucial in applications ranging from automotive cooling systems to data center thermal management, where space and energy consumption are critical factors.
Future trends also point towards the integration of smart technologies within microchannel heat exchangers. The incorporation of sensors and IoT capabilities will allow for real-time monitoring and optimization of thermal performance, enabling systems to adapt to varying operational conditions efficiently. Furthermore, advancements in simulation and design tools will facilitate the customization of microchannel designs, ensuring that they meet specific application requirements while maintaining efficiency. As these trends continue to unfold, microchannel heat exchangers are poised to play a pivotal role in the quest for sustainable and efficient cooling solutions in the years to come.
| Dimension | Value |
|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | 30% higher than conventional exchangers |
| Space Requirement | Up to 50% less space needed |
| Weight | 40% lighter than traditional models |
| Fluid Flow Rate | Increased flow rates by 20% |
| Maintenance Frequency | Reduced by 25% |
| Operating Temperature Range | -50°C to 150°C |
| Cost Savings | 10-15% operational cost reduction |
| Adoption Rate Increase (2023) | Estimated at 25% in industry |